Reference¶
Access Levels¶
TriplyDB uses Access Levels that determine who can access content.
Access Levels can be specified for the following content:
- Datasets, including everything that exist at the dataset level, such as metadata, settings, graphs, and services.
- Queries
- Stories
Access level control¶
The Access Level control (see Figure 1) is available on the settings page for these content types. The Access Level control also appears on the create dialog for these content types. The standard Access Level is always "Private". An explicit user action is needed to set the Access Level to "Internal" or "Public".
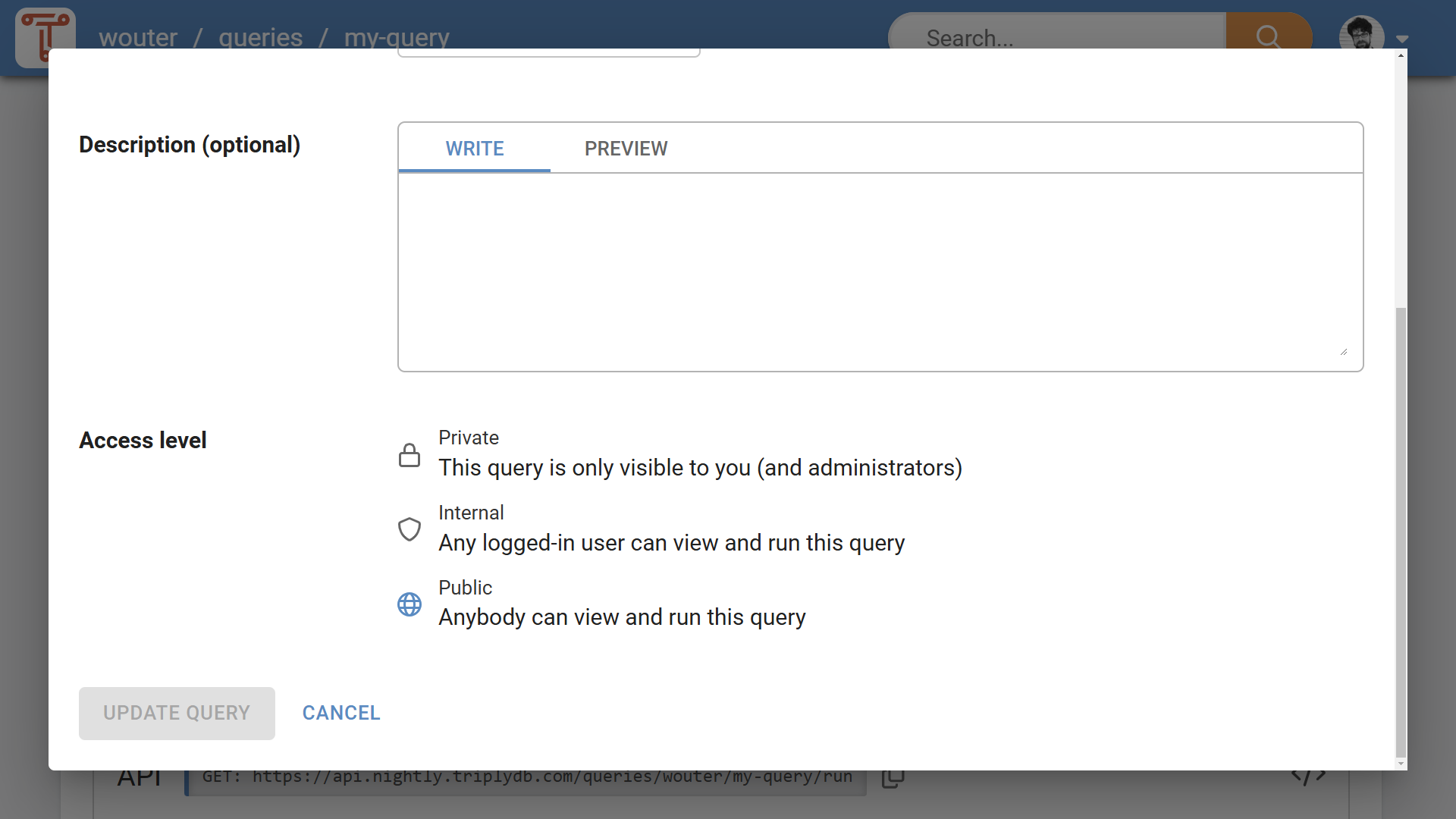
Access Level meaning¶
What an Access Level means, depends on whether content belongs to a user or to an organization. The following table contains the meaning of the Access Levels for content that belongs to a user:
| Icon | Access Level | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
 |
Private | Content is only accessible to you. |
 |
Internal | Content is accessible to anyone who is logged into the same TriplyDB environment. |
 |
Public | Content is accessible to anyone on the Internet. |
The following table contains the meaning of the Access Levels for content that belongs to an organization:
| Icon | Access Level | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
 |
Private | Content is only accessible to organization members. |
 |
Internal | Content is accessible to anyone who is logged into the same TriplyDB environment. |
 |
Public | Content is accessible to anyone on the Internet. |
Access Levels cannot be specified for the following content. This means that this content is always publicly accessible:
- Organizations, including their metadata and members.
- Users, including their metadata.
Access Level dependencies¶
The Access Levels for datasets, queries, and stories may affect each other. For example, a public query may use a private dataset. This means that visitors who are not logged in, can see the query, its metadata, and its query string; however, such visitors will never receive query results from the private dataset. This ensures that private content always stays private, as intended.
A warning is shown to the user when a dependency is introduced to content with a stricter Access Level (see Figure 2). This allows the user to change the Access Levels to a consistent state.
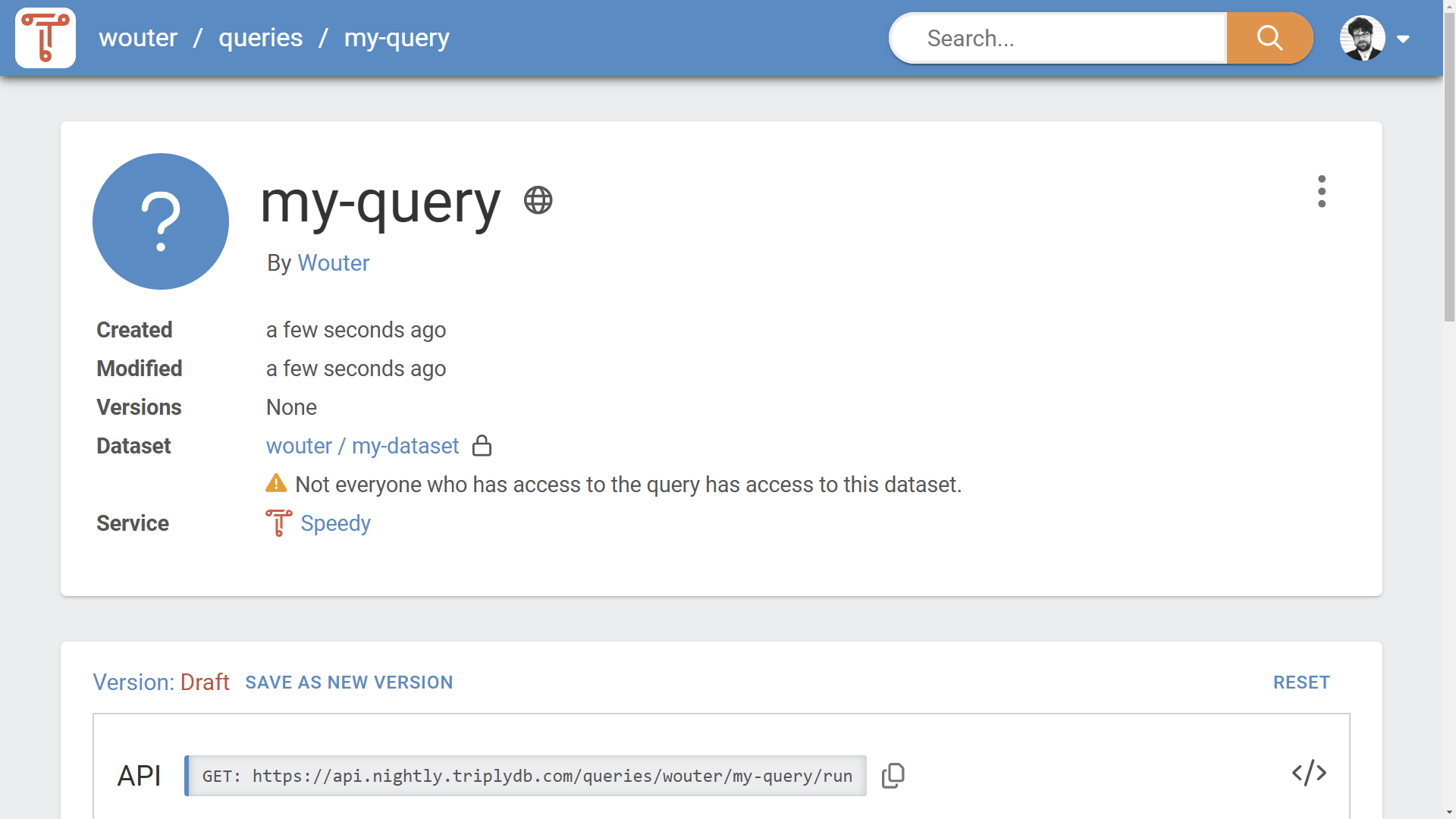
Access levels and workflows¶
These access levels are often used for the following workflow:
- You create a new dataset/query/story starts with access level ‘Private’.
- As the dataset/query/story progresses, give it access level ‘Internal’ to receive feedback from other users.
- Once the dataset/query/story is ready, give it access level ‘Public’ to publish it to the world.
Markdown support¶
Triply allows rich text formatting to be used in the following places:
- Dataset description
- Account description
- Saved Query description
- Data Story elements
- Site welcome message
The following Markdown elements are supported:
Headings¶
Headings are used to divide a text into different sections. The hash
character (#) at the beginning of a line indicates a heading is
used. Multiple hash characters indicate nested headings.
# Heading 1
## Heading 2
### Heading 3
#### Heading 4
##### Heading 5
###### Heading 6
Text styling¶
| Style | Syntax | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Bold | **bold** |
bold |
| Italic | _italic_ |
italic |
| Strikethrough | ~~strikethrough~~ |
~~strikethrough~~ |
Hyperlinks¶
| Style | Syntax | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Raw URL | <https://triply.cc> |
https://triply.cc |
| Labeled URL | [label](https://triply.cc) |
label |
Notice that URLs can also be relative. This allows you to refer to other datasets, saved queries, etc. by using relative paths.
Code¶
There are options for formatting in-line code as well as multi-line code blocks.
In-line code¶
Code can also be used in-line with single backticks:
Use `code` inside a sentence.
Multi-line code blocks¶
Multi-line code blocks start and end with three consecutive backticks. The following Markdown denotes two lines of Turtle:
select * { graph ?g { ?s ?p ?o. } }
The above is rendered as follows:
select * {
graph ?g {
?s ?p ?o.
}
}
Code language¶
The opening backticks are optionally following by the name of the code language. The following code languages are supported:
| Language | Syntax |
|---|---|
| SPARQL | sparql |
| Turtle | ttl |
| TypeScript | typescript |
| R | r |
| Python | python |
The other supported languages are: Bash (bash), C (c), C++
(cpp), C# (csharp), Extended Backus-Naur Form (ebnf), Go (go),
Haskell (haskell), Java (java), JavaScript (javascript), LaTeX
(latex), Makefile (makefile), Markdown (markdown), Objective C
(objectivec), Pascal (pascal), Perl (perl), Powershell
(powershell), Prolog (prolog), Regular Expression (regex), Ruby
(ruby), Scala (scala), SQL (sql), Yaml (yaml).