Uploading Data¶
This section explains how to create a linked dataset in TriplyDB.
Creating a new dataset¶
You must be logged in before you can create a new dataset.
Opening the “Create dataset” dialog¶
You can create a new dataset in either of the following two ways:
-
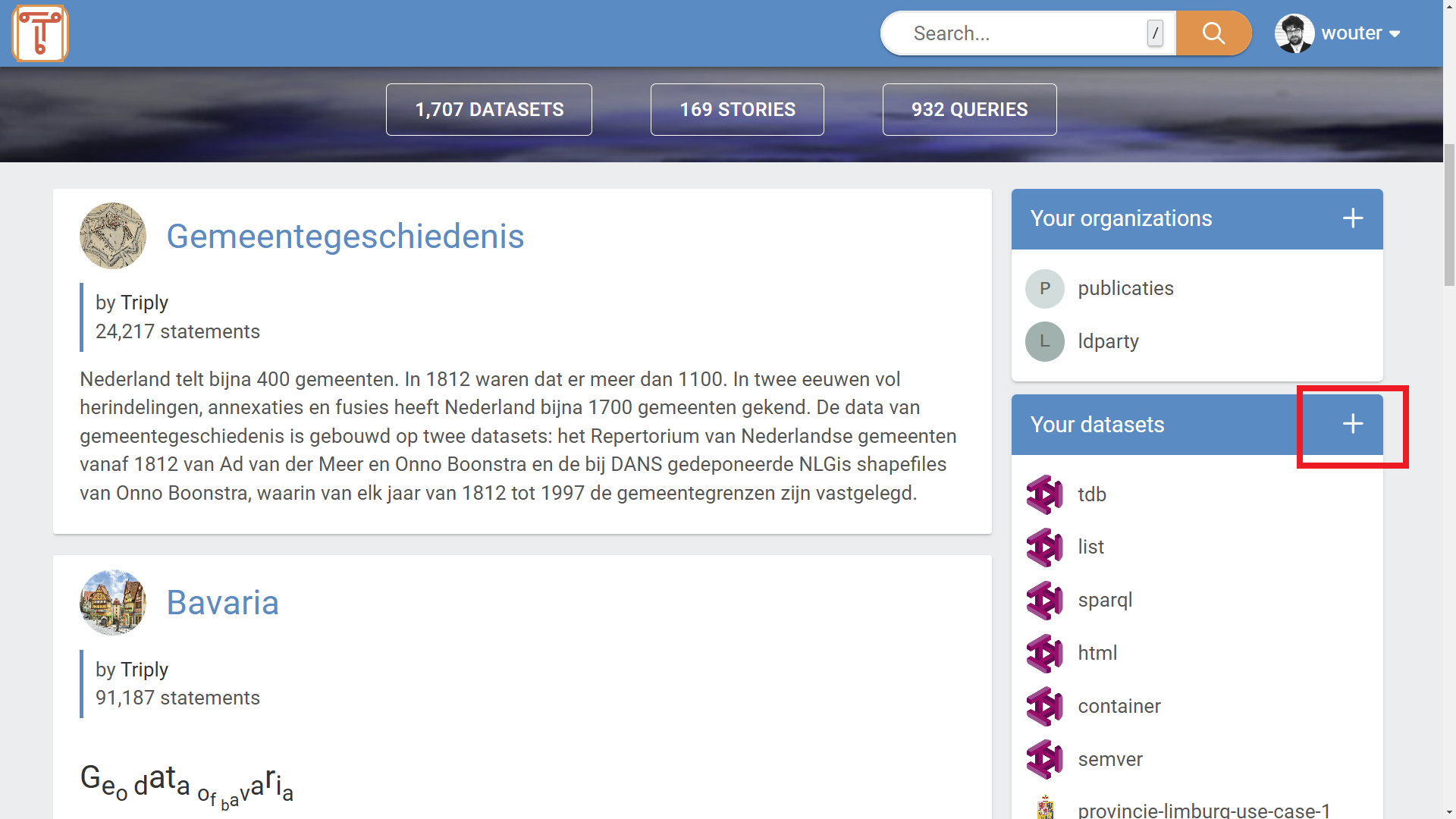
From the home screen (see Figure 1a), click on the
+button next to "Your datasets", on the right-hand side of the screen. -
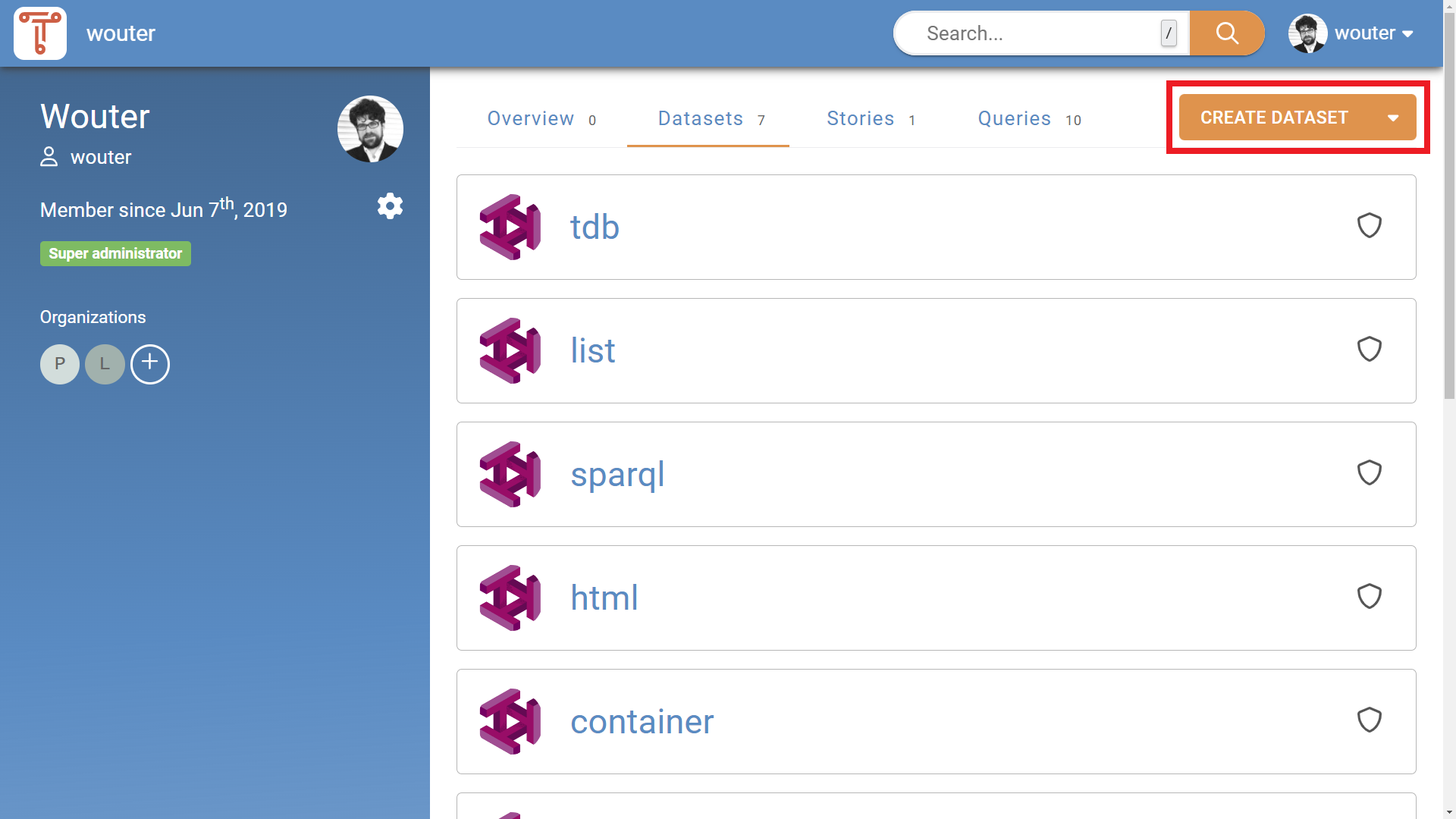
From the user screen (see Figure 1b), click on the “Create dataset” button on the right-hand side.
Inside the “Create dataset” dialog¶
This opens the “Create dataset” dialog (see Figure 2).
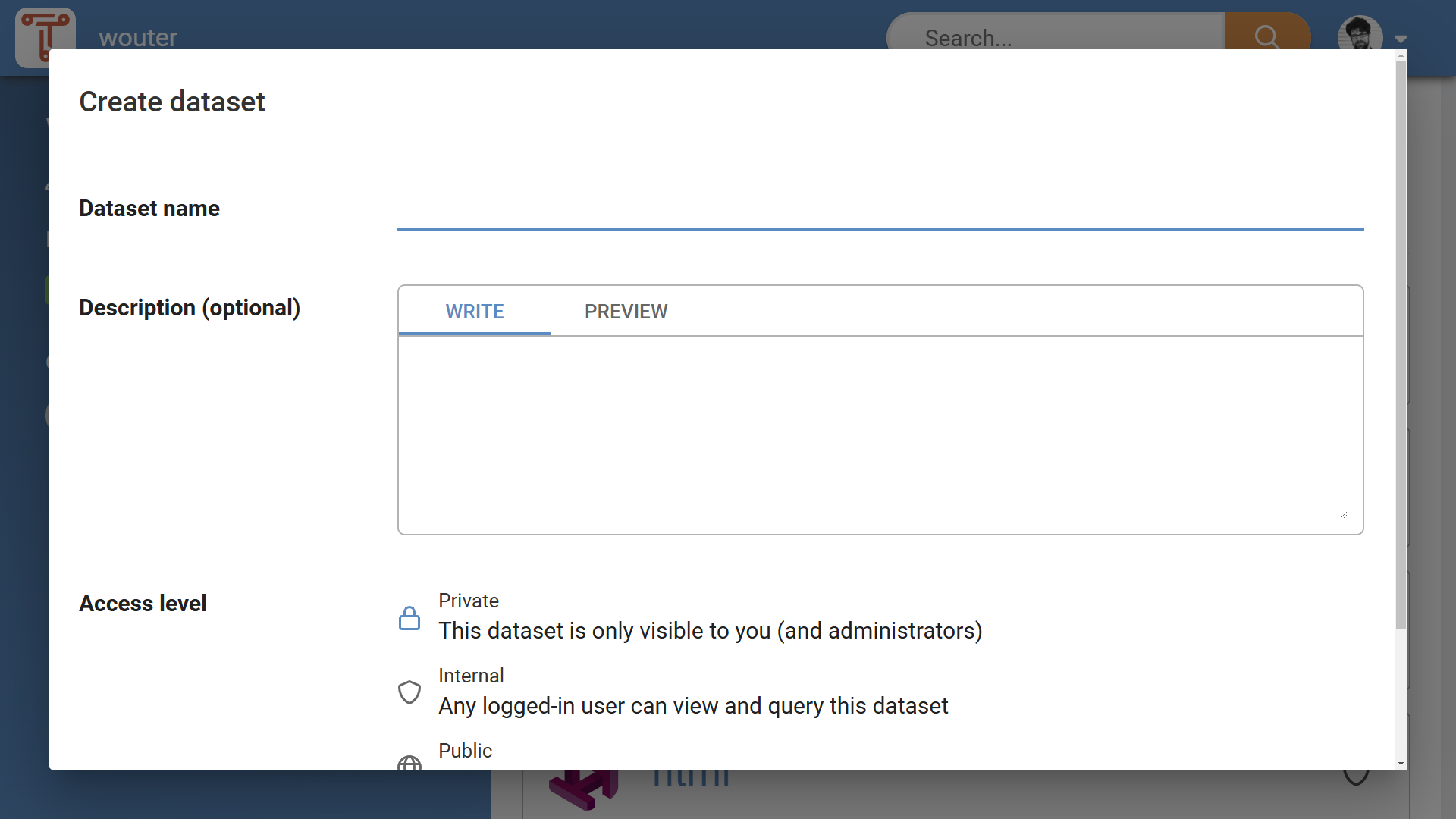
In the “Create dataset” dialog, perform the following steps:
-
Required: Enter a dataset name. A dataset name can contain letters, number, and hyphens.
-
Optional: Enter a dataset display name. The display name will be shown in the GUI and will be included in dataset metadata.
-
Optional: Enter a dataset description. This description will be shown in the GUI, and will be included in dataset metadata. The description can be formatted with Markdown. See Section Markdown for details.
-
Optional: Change the access level of the dataset. The standard access level is “Private”. See Section Dataset Access Levels for more information.
This creates a new dataset, and displays the “Add data” page (see Section Adding data).
Adding data¶
You must first have a dataset, before you can add data. See Section Creating a new dataset for more information.
Opening the “Add data” pane¶
You can open the “Add data” pane in either of the following two ways:
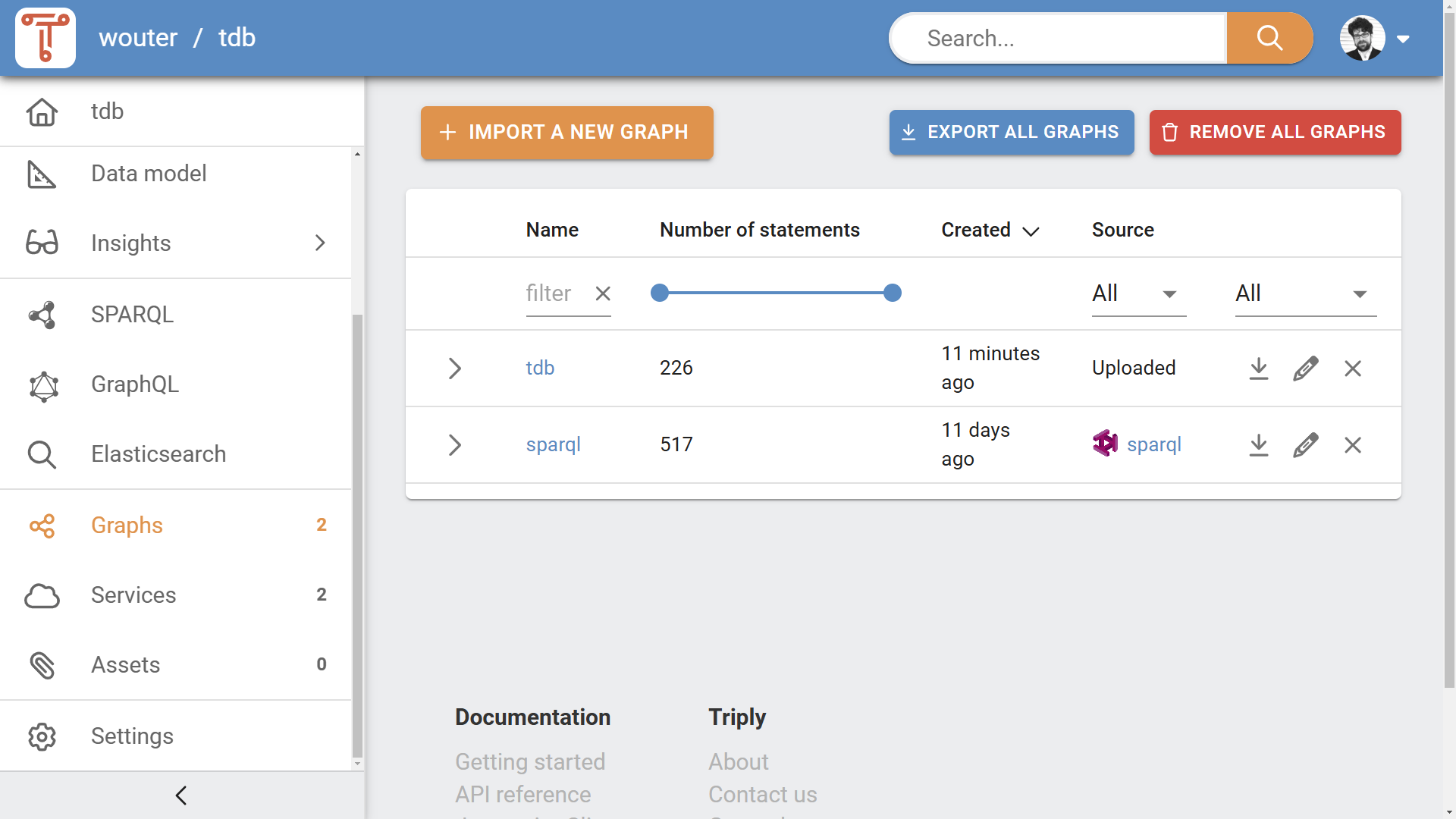
- From the Graphs page, click on the "Import a new graph" button (see Figure 3a). This opens the "Add data" pane.
- When a dataset does not have any data yet, a message is displayed on the dataset homepage (see Figure 3b) that can be clicked. This opens the "Add data" pane.
- After creating a new dataset, the "Add data" pane is automatically opened.
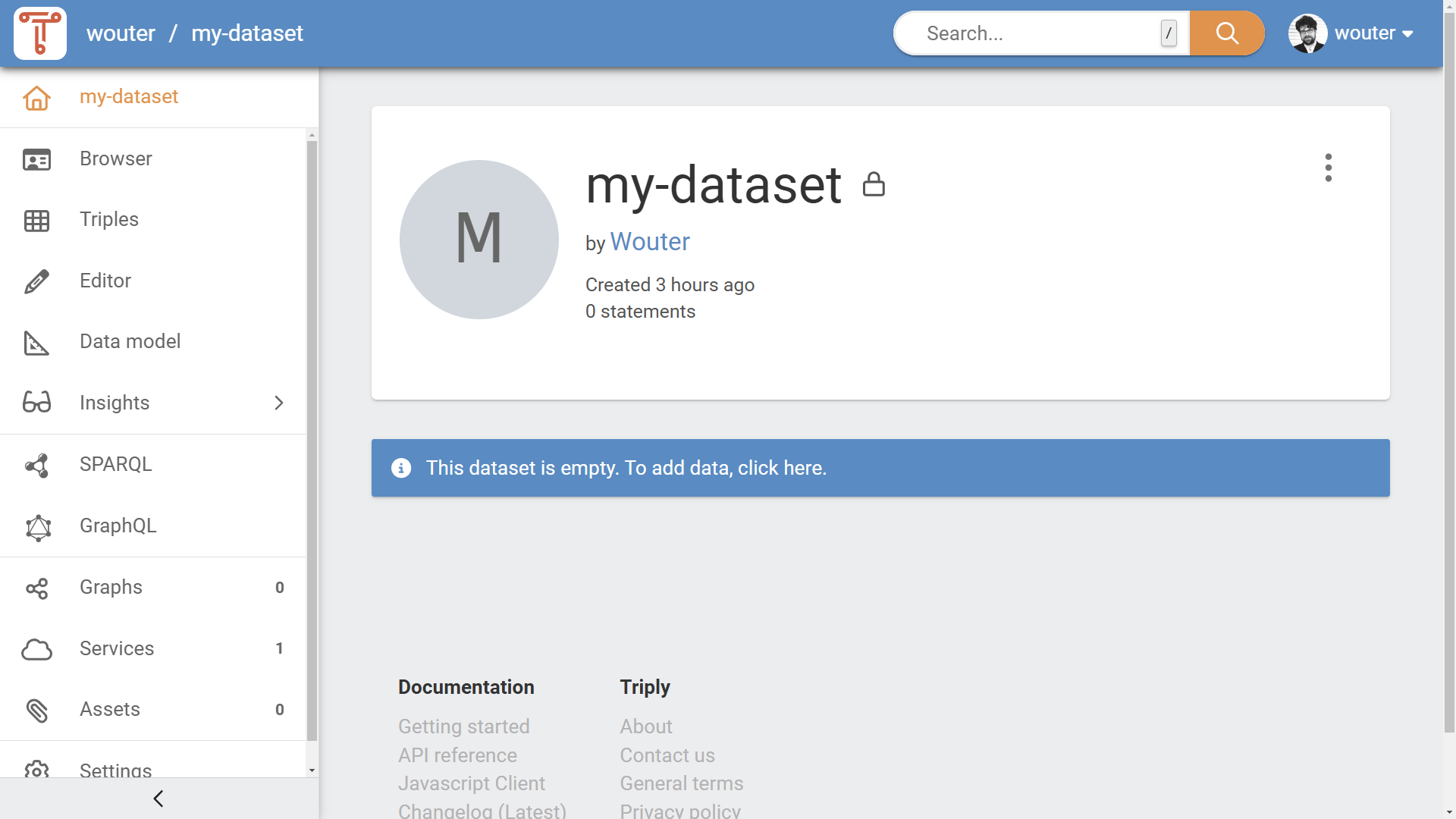
Inside the “Add data” pane¶
The “Add data” pane is now displayed (see Figure 4).
In the "Add data" pane, choose one of the following approaches for adding data:
- "Add data from an existing dataset"
- Search for data from a dataset that you have access to in the TriplyDB system. After you have found a dataset, you can choose which graphs to add. See Section Add data from an existing dataset for more details.
- "Add data from URL"
- Enter a URL to a data file that is published online. The URL must be publicly accessible. The URL must point to a file that contains RDF or CSV data. See Section Add data from a URL for more details.
- "Add data from files"
- Click the cloud icon to open a file explorer window, in which you can select one or more files from your computer. Alternatively, drag-and-drop the local files from your computer onto the cloud icon with the upward pointing arrow. Files must contain RDF or CSV data. See Section Add data from files for more details.
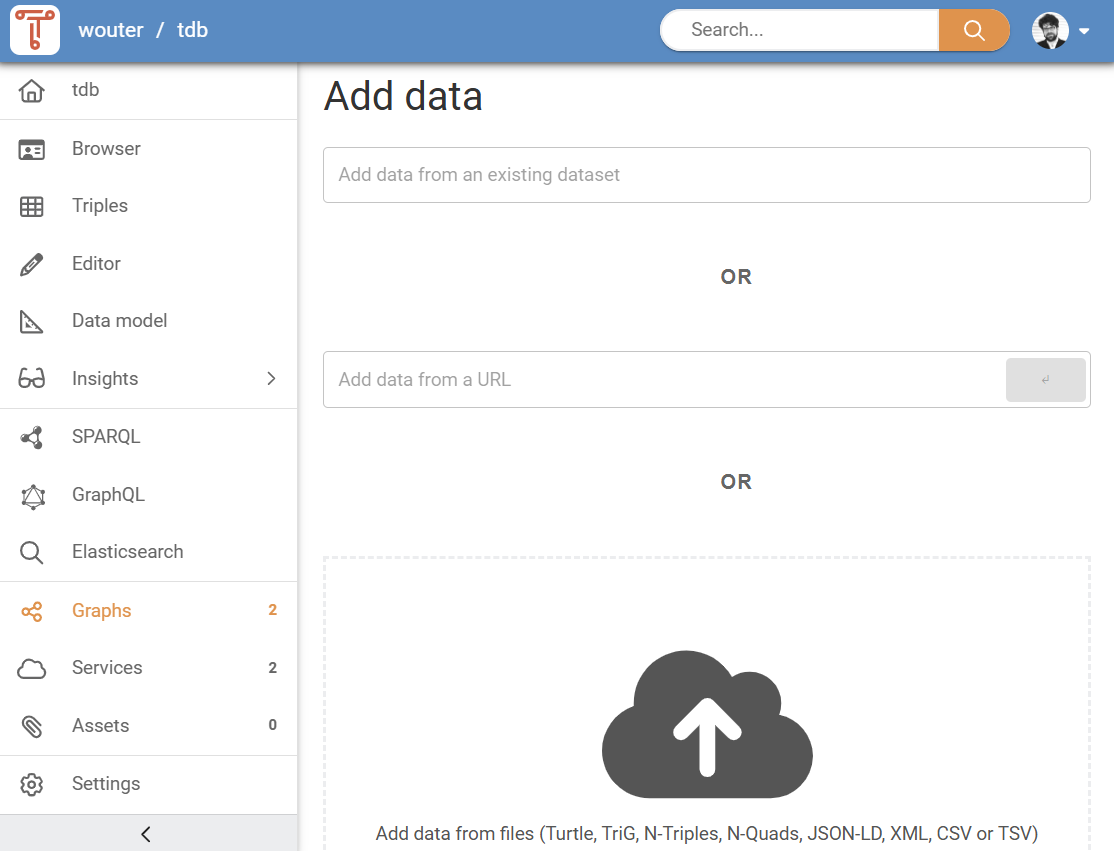
Add data from an existing dataset¶
The first option for adding data is to add it from datasets that are already published in the same TriplyDB instance. This is done with the “Add data from an existing dataset” field. By typing in this field, a dropdown list of existing datasets is shown (see Figure 5).
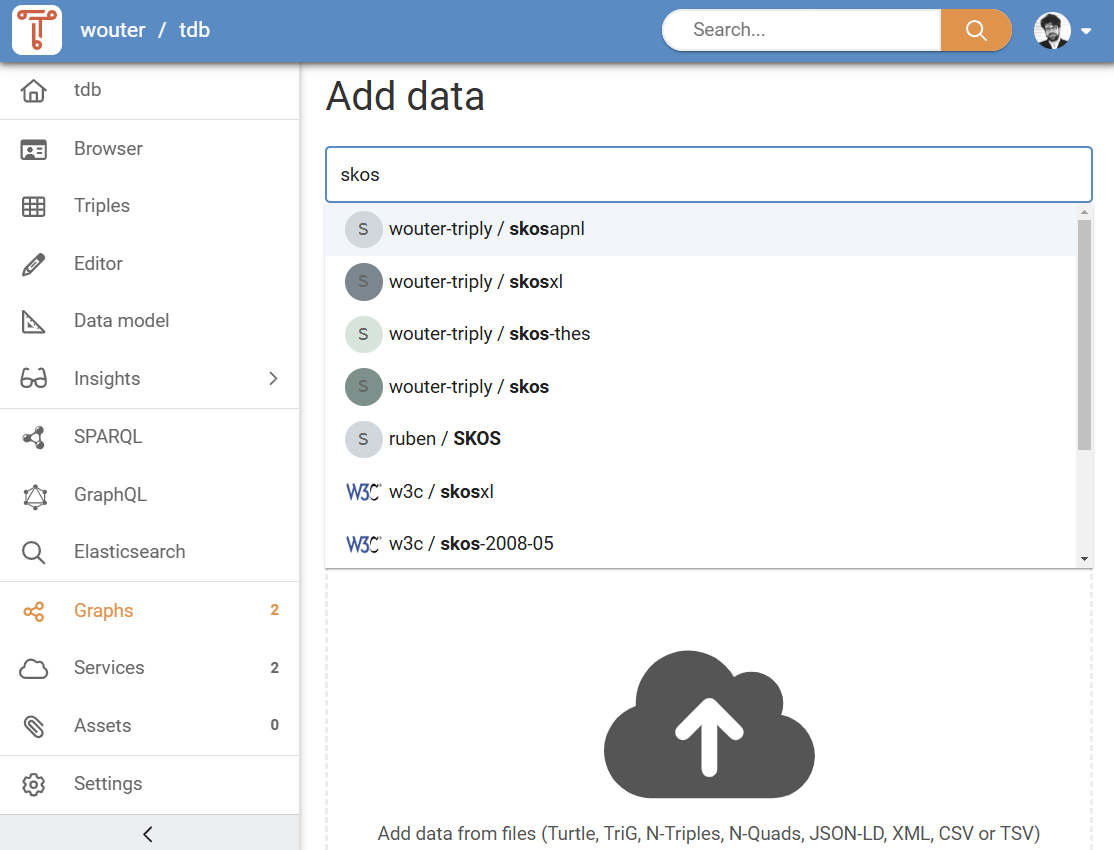
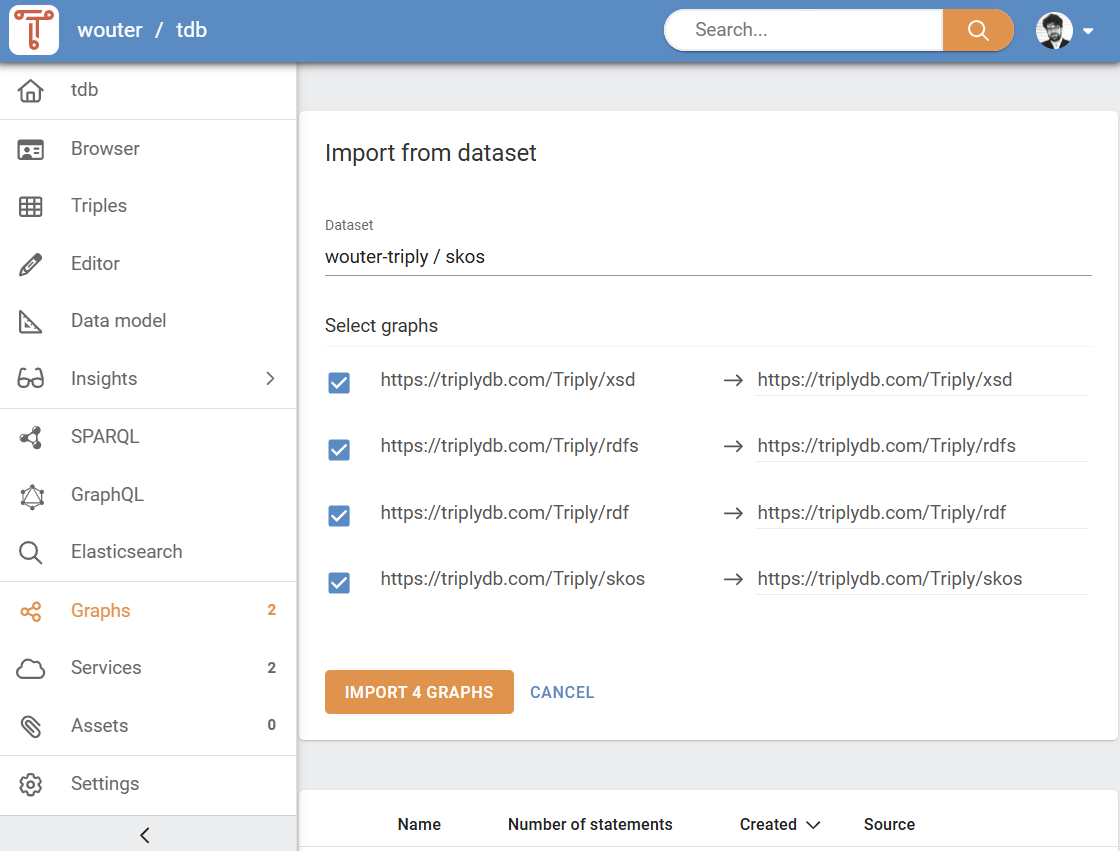
Once the correct dataset appears in the dropdown list, click it to select it. This will open the "Import from dataset" pane (see Figure 6). You can choose which graphs to import from the existing dataset. Click "Import graphs" to start importing from an existing dataset. Moments later, the graphs are added to your dataset.
Add data from URL¶
The second option for adding data is to add it from an online URL. This is done by entering the URL inside the “Add data from a URL” text field (see Figure 7). After you have entered the URL, click the orange button on the right to start adding data. The data is now being downloaded to your dataset. How long this takes depends on the size of the data and the speed of the remote server where the data is retrieved from.
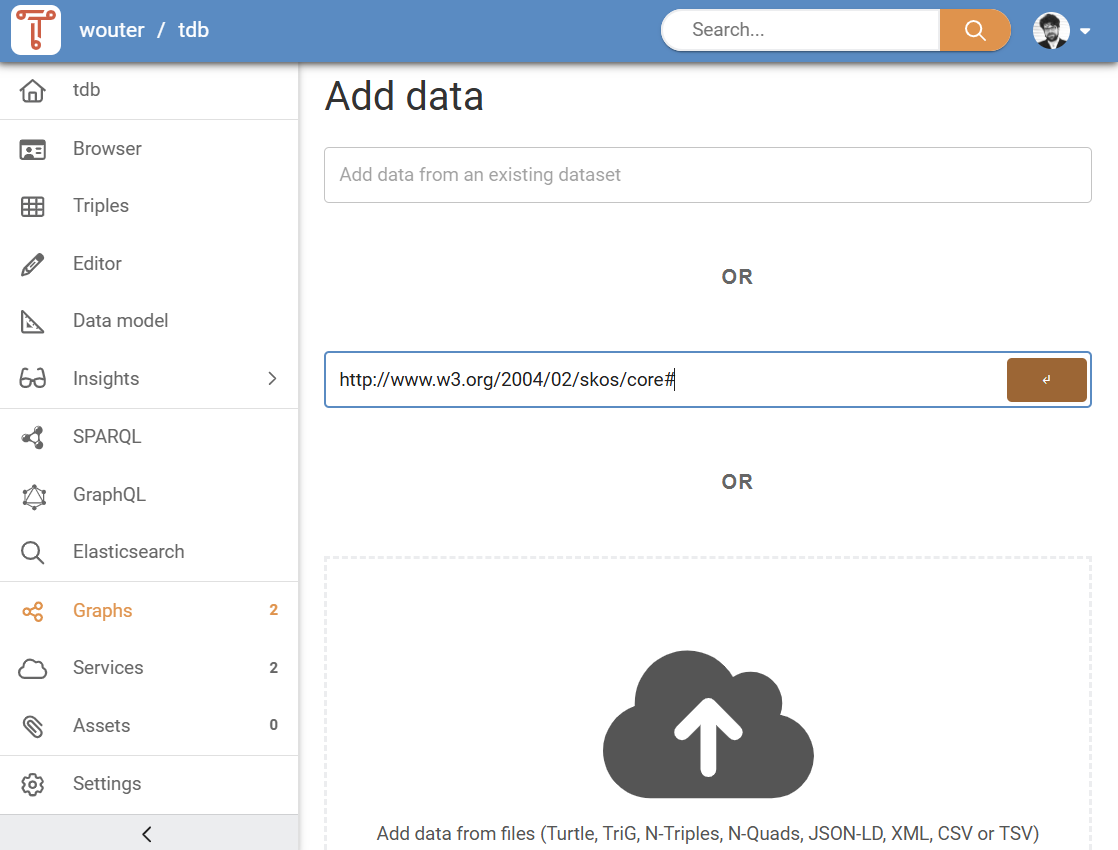
Only URLs that contain supported data formats will be added. See Section Supported data formats for more information.
Add data from files¶
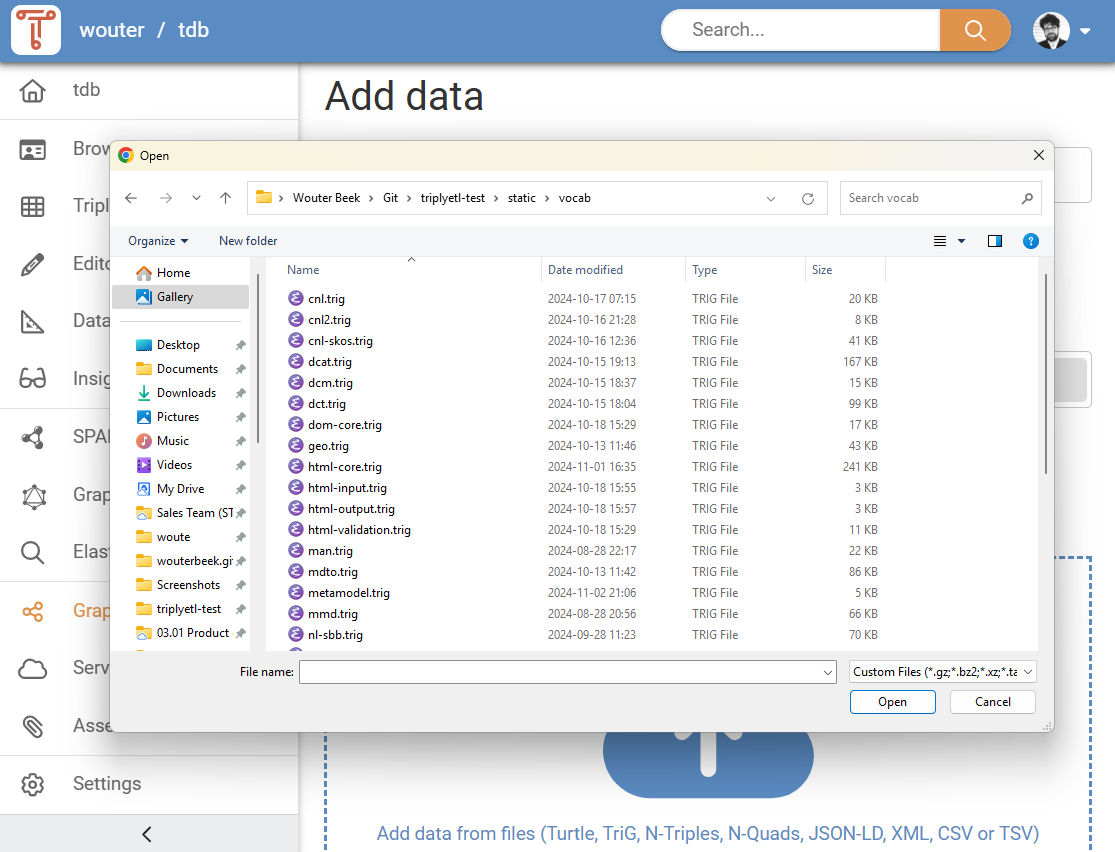
The third option for adding data is to add it from files that are on your computer. This can be done in two ways:
- Click the cloud icon to open a file finder dialog. Here you can select one or more files from your computer (see Figure 8). The file finder dialog that opens, depends on your Operating System. In Figure 8, the Windows file finder dialog is shown.
- Drag-and-drop one or more files from your computer onto the cloud icon with the upward pointing arrow.
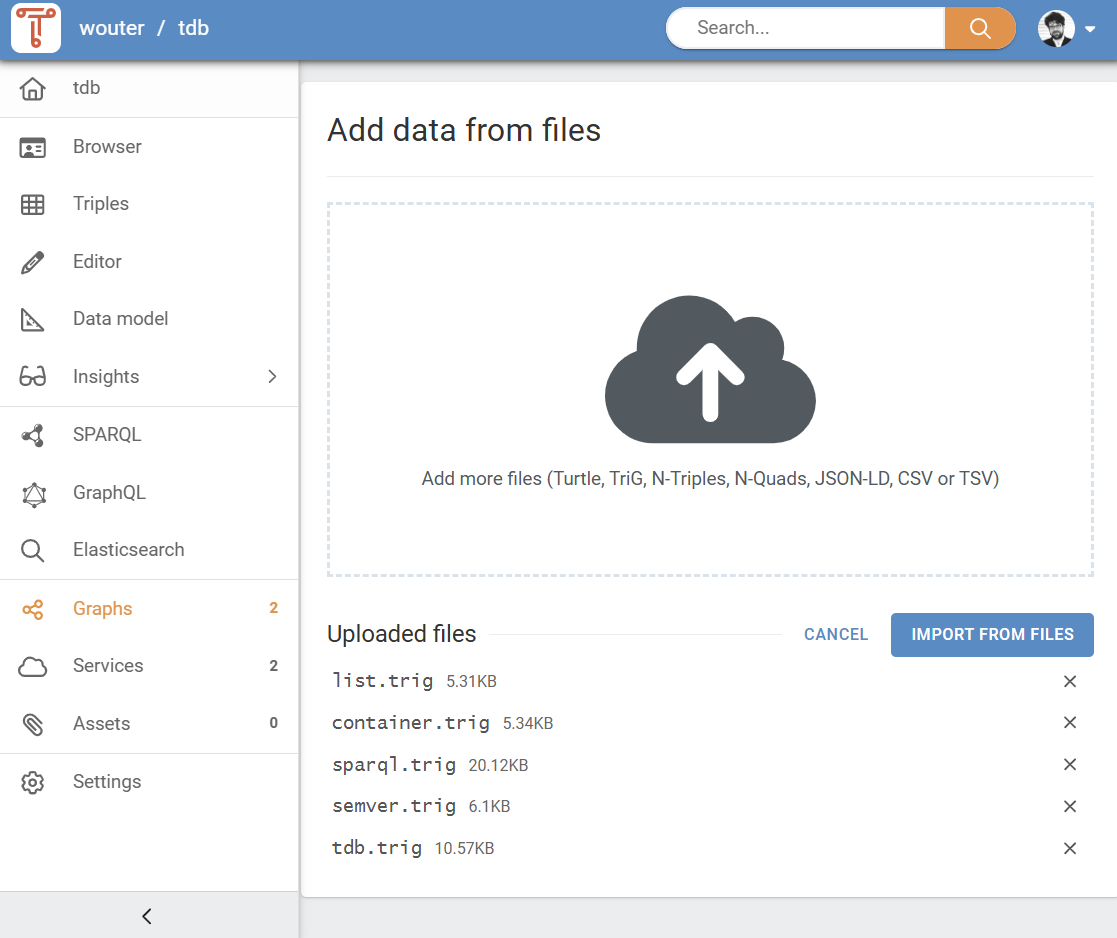
After you have added one of more files, a list of uploaded appears (see Figure 9). You can add or remove more files, until you have the complete upload job configured. Once the list of files is complete, you can click "Import from files" to start adding data from files. How long this takes depends on the size of the data.
Only files that contain supported data formats will be added. See Section Supported data formats for more information.
Supported data formats¶
Files must contain RDF and/or CSV data, and must use one of the supported file name extensions:
| Data Format | File name extension |
|---|---|
| Comma-Separated Values (CSV) | .csv |
| JSON-LD | .jsonld, .json |
| N-Quads | .nq |
| N-Triples | .nt |
| RDF/XML | .rdf, .owl, .owx |
| TriG | .trig |
| Turtle | .ttl, .n3 |
It is possible to upload up to 1,000 separate files in this way. When you have a lot of files and/or large files, it is better to compress them into an archive format. This allows an any number of files of any size to be uploaded. The following archive/compression formats are supported:
| Archive format | File name extension |
|---|---|
| gzip | .gz |
| bzip2 | .bz2 |
| tar | tar |
| XZ | .xz |
| ZIP | .zip |
Adding malformed data¶
TriplyDB only allows valid RDF data to be added. If data is malformed, TriplyDB will show an error message that indicates which part of the RDF data is malformed (see screenshot). If such malformed data is encountered, the RDF file must first be corrected and uploaded again.
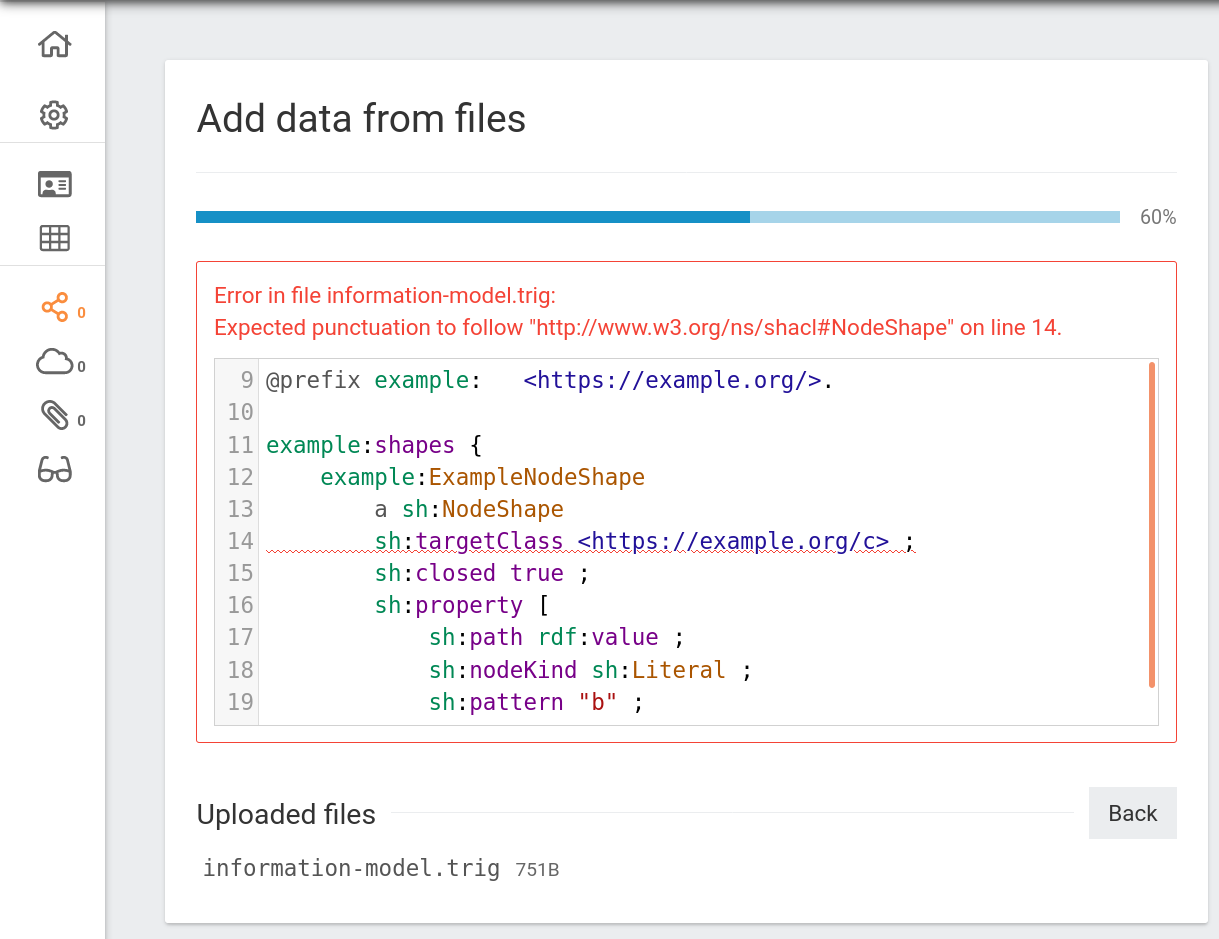
TriplyDB follows the linked data standards strictly. Many triple stores allow incorrect RDF data to be added. This may seem convenient during the loading phase, but often results in errors when standards-compliant tools start using the data.
Assets: binary data¶
Not all data can be stored as RDF data. For example images and video files use a binary format. Such files can also be stored in TriplyDB and can be integrated into the Knowledge Graph.